Overview
Our heart is essentially a pump that supplies oxygenated blood to all the muscles in the body so that they can function properly and do their jobs to maintain their role in the physiological environment. The heart is also a muscle, and therefore it also needs the supply of oxygenated blood to continue performing their work without any hindrance. These arteries are also known as coronary arteries.
Somehow, if your coronary arteries are blocked by plaque or some other reasons, then your heart muscle will not receive the necessary oxygen and the nutrients to function properly. If this condition is left unattended, the heart would finally seize to function and that would be a cause of heart attack.
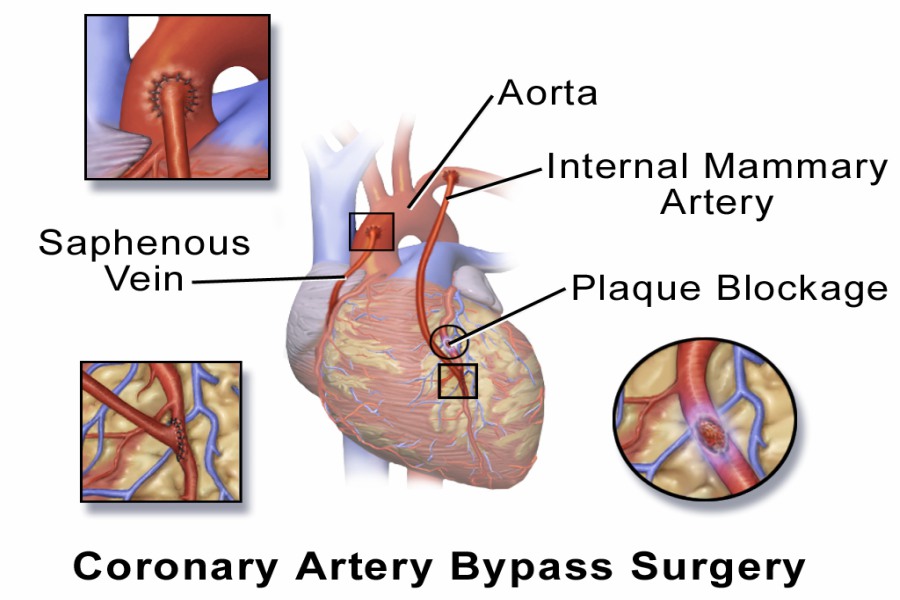
To solve this situation, the physician may choose to perform a surgery where he or she can open an alternative pathway to let the clogged up blood flow to its destination. This “bypass” in the coronary arteries is done with the help of an artery from another part of the body of the patient, preferably from the thighs. Although this may relieve the pain, discomfort, or the symptoms, this will not solve the actual reason that necessitated the application of this procedure.
Why it’s needed?
Coronary arteries are important arteries in the context that they supply the heart itself with the necessary oxygen and nutrition to keep it pumping, and the heart presents the other organs with the nutrition and oxygen to keep them working. Whenever there is a block on the coronary arteries, the chance of the patient suffering a heart attack increases by several folds. The cardiologist taking care of you can suggest a CABG for the following reasons;
- You are experiencing intense chest pain due to the contraction of multiple blood vessels that supply your cardiac muscle, leaving the muscle with lesser blood during light physical activities or even at rest.
- You have multiple unhealthy coronary arteries, and the heart's main pumping compartment, namely, the left ventricle, isn't running well.
- You have an artery obstruction for which angioplasty (temporarily inserting and inflating a tiny balloon to widen the artery) isn't proper, you've undergone an earlier unsuccessful angioplasty or stenting (placement of a small wire mesh tube to hold the artery open), or you've had stent placement, but the artery has suffered restenosis (narrowing down again).
SYMPTOMS
A CABG procedure is needed to make a substitute route for a coronary artery where the blood flow has been blocked due to the deposition of plaques narrowing the artery. This condition is known as atherosclerosis and may be caused due to the following factors;
- High levels of LDL: LDL, or low-density lipoprotein, is a major cause of the formation of plaques in the artery. High levels of it in the blood will quicken the formation of plaques.
- Low concentration of HDL: HDL, or High-Density Lipoprotein, is known to remove the plaques from the arteries. Low levels of HDL will hasten the formation of plaques in the blood vessels.
- Unhealthy lifestyle: Ingesting a lot of fast foods, and not having a routine of the meals may cause the blocks to form in the cardiac arteries.
- Smoking: Puffing cigarettes and that too without exercising caution, can cause the speeding up of the formation of plaques in the cardiac arteries.
- Increased circulating blood sugar: People with diabetes have an increased chance of developing plaques in the arteries than those without. Even, the people with high blood sugar but still not at the level of alarm are not safe from his particular cardiac event.
- Stress: Ongoing stress has been known to cause plaques in the heart.
- Obesity: An obese person is at more risk than developing blockage and getting a CABG than a person with a normal BMI (Basal Metabolic Index).
The symptoms that suggest a blockage in the cardiac arteries are not specific and can be a marker for any blood disease. However, the most common symptoms that can arise at the event of 70% blockage of the heart can be listed as;
- Pain in the chest or Angina
- Difficulty in breathing
- Quickened heartbeat
- Weakness or dizziness
- Nausea
- Excessive sweating
- Inability to move a limb
- Overlapping of words.
- Cold feet
- Delayed healing of leg injuries.
DIAGNOSIS
There are several tests for clogged arteries that can be helpful in determining the extent of the damage and help the physician to make the decision of using the CABG procedure. Depending upon your medical history, the surgeon may go for any of the following tests;
- Cholesterol screening: Biochemical tests to determine the level of cholesterol in the body.
- Chest X-ray: using X-ray or low wavelength light to take an image of the heart.
- CT scan: Applied for getting a comprehensive picture of the inner parts of the body.
- Ultrasound: Sound waves with high frequency are used for finding the internal picture of the patient’s body.
- Echocardiogram and/or cardiac stress test: Tracking the response of the heart through administering stress and measuring the different cardiac outputs like heart rate, pulse rates, and breathing frequencies.
- Electrocardiogram: Using the electrical field and its activity to measure any abnormality in your heart.
- MRI or PET scanning: Using magnetic fields to determine any abnormality in the heart.
- Angiogram: Testing for any blockages forming in the cardiac tissues.
After bearing in mind the obtained data from the different investigations, the physician may opt to perform the CABG procedure or not.
RISK FACTORS
This protocol has risks associated with them as they are invasive and require a prolonged duration of external exposure. The risks may include;
- Bleeding
- Heart rhythm problems.
- Blood clots.
- Chest pain or difficulty breathing
- Infection at the incision site
- Kidney or renal failure.
- Reactions to anesthesia.
- Death
POST-OPERATIVE CARE
Depending upon the state of the patients, the recovery rate may vary. However, the surgeon will prescribe different steps for you to follow without fail. Usually, the patient can leave the hospital after four to five days. Normally after the operation, the patient may be kept in an ICU for observation for a day or two.
Through this time, he or she will be connected to the heart, blood pressure, body temperature, and inhalation monitors. After the restoration of motor functions, he or she may be transferred to a general ward. Other things you may need to take care of will be;
- You may feel constipated after the operation, which is normal. Medicines or change in diet can correct that.
- You may have difficulty sleeping, which is also normal and the physician can give you sleeping pills.
- You may have swelling at the site of surgery and may be given painkillers for that.
- You will have to give up smoking
- Take LDL lowering medicines.
- Having a healthy lifestyle and weight.
- Adding more vegetables, whole grains, and fruits to your diet and reducing saturated fat.
- Take less stress and if necessary, take cardiac rehabilitation.
TREATMENT
The treatment protocol especially for this surgery is divided into three parts and must be followed without fail by the patient for the right managing. The time-points can be divided as;
Before the procedure
You need to check with your physician for the continuance or holdup of taking any medication, especially for diabetes, if any. Around two to three weeks before the time, you will also need to entitle someone for collecting you from the hospital. If you have a health cover or insurance, inform the executives and the business department of the hospital for due action. Your physician may perform some pre-operative tests and suggest some additional medicines.
Before the surgery, you must have a complete bowel movement and may have to skip any food or beverages. The hospital staff may shave off the hair from the incision region and remove ornaments, powder and paint, and other decorations before the operation.
During the procedure
The operation could be done in multiple ways, although traditionally, CABG is performed by open-heart surgery. The techniques that may be used for performing this surgery are;
Open-heart surgery (on-pump)
- You will be taken to the operation theater and rested in the operating table.
- You will be given general anesthesia to make you unconscious.
- Your heart will be connected to a heart-lung machine.
- A ventilator machine will do the breathing for you.
- The surgeon will cut down the center of the chest, along the sternum.
- He or she then will spread open the rib cage to uncover the heart.
- After the chest is opened, the heart is temporarily stopped with medication.
- The surgeon will take a section of a blood vessel in good physical shape, often from inside the chest wall or from the lower leg.
- He or she will attach it at both ends of the obstructed artery so that blood flow is relayed around the narrowed part of the faulty artery.
- After completing the surgery, the surgeon will restart your heartbeat, disconnect the heart-lung machine and close your chest bone.
- The wire used to do so will persist in your body after the bone patches up.
Open-heart surgery (off-pump)
This procedure is done while the heart still beats and the area of interest is stabilized using special equipment. This is a risky procedure and is not performed for everyone.
Minimally invasive surgery
Here the surgery is performed using small incisions and often with robotic assistance and video imaging. A small area of the patient is needed to operate upon.
Depending upon the state of the patient, the surgery may take up to six hours.
FACTORS AFFECTING COST
The cost of the surgical procedure will be influenced by on the following;
- The type of hospital chosen
- The operating room charges
- The fee of the surgeon
- The instrument and medicine charges
- The charges prevalent and number of days spent in the ICCU and recovery room post the procedure
FAQ
Depending upon the health, follow-ups, and lifestyle of the patients, a range of five to ten years is common.
For multiple obstructions in the arteries, it has been seen that CABG is more effective than a stent in patients with cardiac ailments.
No, it is very difficult to release arteries from a blockage in the diseased patients. However, with a healthy diet and lifestyle, additional plaque formations can be prevented.


 Best Hospitals
Best Hospitals












