To get a clear vision of what you see, you need to have a healthy, smooth and clear cornea.
Cornea is a dome-shaped, transparent layer, which, along with the lens of the eye, works together to focus the light to produce a clear vision. If the cornea is damaged, it may affect the vision of a person. If the damaged cornea cannot be repaired or healed, it may need a cornea transplant.
Overview
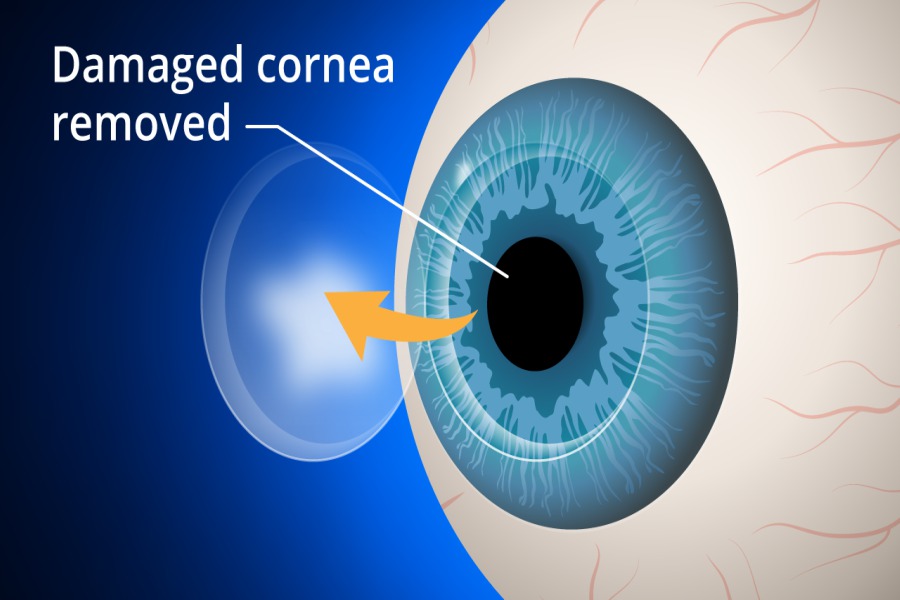
Cornea transplant is a surgical procedure performed to replace the damaged part of the cornea with a healthy cornea tissue from the donor. It can improve the shape and structure of the diseased or damaged cornea, restore the vision and reduce pain.
ELIGIBILITY
A cornea transplant can be performed in any patient who has any of the following conditions:
- Clouding of the cornea
- Fuchs’ dystrophy
- Keratoconus (cornea that bulges outward)
- Thinning of the cornea
- Scarring of cornea due to injury or infection
- Complications due to any former eye surgery
- Swelling of the cornea
PREPARATION BEFORE PROCEDURE
A complete eye examination will be done to evaluate the condition of the eye. The surgeon will also determine the size of the donor cornea that is required. Complete medication and medical history will be obtained. If you have any other eye condition like inflammation or infection, it will be treated before the surgery.
Usually, the cornea for transplant is received from a deceased person. Therefore, whenever the healthy cornea is available, it will be transplanted to the person with the diseased cornea.
PROCEDURE TYPE
Based on the amount of corneal tissue removed, cornea transplant is of two types:
Penetrating keratoplasty (PK): In this method, the entire center part of the damaged cornea is replaced with a healthy donor cornea. It is performed to treat conditions in which the full thickness of the cornea is affected.
Endothelial keratoplasty (EK): In this method, the damaged cornea is removed from the back corneal layers, which includes the endothelium layer and the descemet membrane, a thin layer of the tissue of the endothelium, which protects it from the infection and injury. Once the tissues are removed, the donor tissue is implanted in order to replace the damaged tissue.
There are two subtypes of the procedure:
- Descemet stripping endothelial keratoplasty (DSEK): In this method, one-third of the cornea is replaced by the donor tissue. This method is most commonly used.
- Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK): In this method, a thin layer of donor tissue is used, which makes the procedure bit challenging. Thus, it is rarely performed.
Anterior lamellar keratoplasty (ALK): In this method, the diseased tissue is removed from the front layers of the cornea, which includes the epithelium and the stroma, excluding the back layer of the endothelium. Based on the depth of the cornea damage, the ALK procedure is of two types:
- Superficial anterior lamellar keratoplasty (SALK): In this method, only the front layer of the cornea is replaced, leaving the healthy cornea intact.
- Deep anterior lamellar transplant (DALK): In this method, the cornea is removed from the deeper layers. It is performed in cases when the damaged cornea extends deeper up to the stroma.
ABOUT PROCEDURE
Cornea transplant is performed under local anaesthesia. Once the anaesthesia is effective, the entire thickness of the diseased cornea is cut by trephine (an instrument that works as a cookie-cutter) and an opening is created. In this opening, the cornea is cut and placed. The new cornea is stitched to the place with the help of a fine thread. This thread may be removed during the follow-up visit. The procedure may vary depending upon the type of the method and the extent of the cornea diseased.
POST-PROCEDURE CARE
Once the procedure is done, you may receive medication or eye drops to reduce pain, swelling and prevent infection. An eye patch may be given to you to protect the eye during the healing procedure.
RECOVERY TIPS
Following measures may aid in speedy recovery:
- Use the eye drops or medications as prescribed
- Avoid rubbing or pressing the eye
- Wear sunglasses to protect the eye
- Avoid any injury to the eye
- Slowly return to routine activities
- Go for regular eye checkup in the first year after the surgery
FACTORS AFFECTING COST
The cost of cornea transplant may differ based on the following factors:
- Type of surgery
- Condition of the eye
- Location of the hospital
- Surgeons cost
- Medication
- Post-operative care
- Hospital stay (if required)
FAQ
It usually takes around 45 minutes to complete the cornea transplant procedure.
Keratoprosthesis is the treatment option for people who are not fit for the cornea transplant. In this method, an artificial cornea is inserted in the place of the diseased cornea.
The damaged cornea may show the following symptoms:
- Cloudy vision
- Blurred vision
- Eye pain
The most important complication that is associated with the corneal transplant is the rejection of the donor cornea.
The signs and symptoms associated with the cornea rejection are:
- Pain in the eye
- Redness in the eye region
- Sensitivity to light
- Loss of vision


 Best Hospitals
Best Hospitals












